SAP Process control helps to keep any organization at a low risk level and have an increase in its control and process efficiency. The master data in SAP Process Control keeping things under control, further it enables the user to map the business details in a hierarchical way.
The two master data components which will look similar but are meant to solve two different challenges are regulations and policy. This blog tries to explain an overview of both.
Regulations: The framework of law and rules that have been provided by the legal body is referred to as regulation. Complying with the regulations to follow the best practices and recommendations to mitigate risk and to be in comply with the legal bodies of particular geographical locations where the organization is operating/registered.
Some of the examples are ISO27000, ISO32000, GDPR.
Policy: The Policy is a document which is usually a SOP or the procedure created by an organization to follow the regulations.
(A). Procedure to configure a regulation and add our own regulation to SAP Process Control System
-
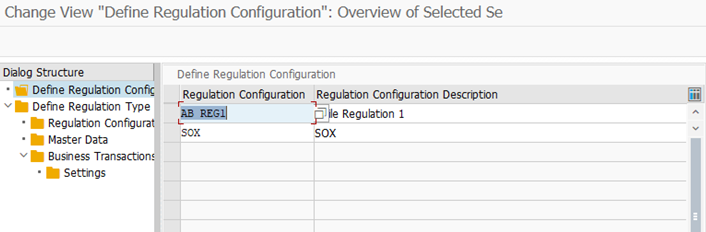
- Configuration of Regulation
SPRO-IMG-GRC-PC-MULTIPLE COMPLIANCE FRAMEWORK-CONFIGURE COMLIANCE INITIATIVES
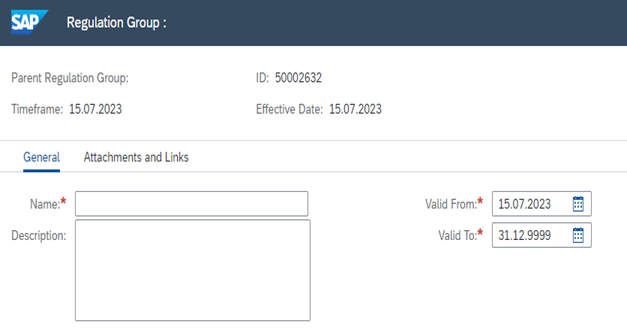
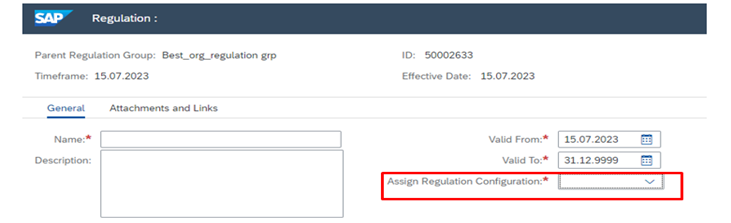
- Creation of Regulation group followed by Regulation in NWBC
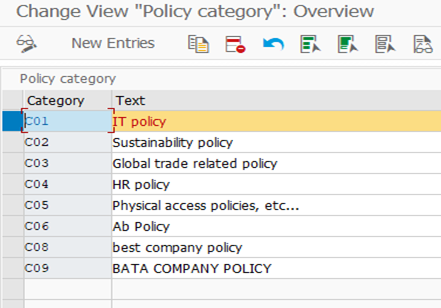
(B). Procedure to define our own policy types.
- Navigation-
SPRO-IMG-GRC-GENERAL SETTING-COMMON COMPONENT SETTING-POLICY MANAGEMENT-MAINTAIN POLICY CATEGORIES
- Policy creation-
SAP Process Control allows us to measure the efficiency of a regulation and policy through frequent scheduling of assessments. DataNub technologies, being a leader in providing expert solutions & services in compliance space can help organizations to stay ahead of curve in handling any cybersecurity & compliance issue or threats.