Introduction:
- SAP Identity Access Governance (IAG) is a solution that helps organizations manage the access rights of their users across various SAP and non-SAP systems. IAG enables the automation, monitoring, and governance of user access, as well as the detection and remediation of access risks. IAG can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements, improve security, and reduce operational costs.
- However, implementing and operating IAG also involves some potential risks that need to be identified and mitigated. These risks can be categorized into four main areas: technical, functional, organizational, and compliance. This document provides an overview of these risk areas and some best practices to address them.
Technical Risks:
Technical risks are related to the infrastructure, performance, availability, and security of the IAG solution. Some examples of technical risks are:
- Hardware or network failures that affect the availability or performance of the IAG solution
- Software bugs or configuration errors that cause malfunctions or data inconsistencies in the IAG solution
- Cyberattacks or unauthorized access that compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the IAG solution or the data it processes
- Integration issues or compatibility problems with other systems or applications that interact with the IAG solution
Some best practices to mitigate technical risks are:
- Design and implement a robust and scalable architecture for the IAG solution, following the SAP recommendations and guidelines
- Perform regular backups and disaster recovery tests to ensure the availability and recoverability of the IAG solution and the data it processes
- Apply the latest patches and updates to the IAG solution and the underlying components to fix any known issues and vulnerabilities
- Monitor and test the performance and functionality of the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, and resolve any issues promptly
- Implement and enforce strong security policies and controls to protect the IAG solution and the data it processes from unauthorized access or misuse
- Document and review the technical configuration and settings of the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, and maintain a change management process to track any modifications
Functional Risks:
Functional risks are related to the business processes, workflows, and rules that are supported by the IAG solution. Some examples of functional risks are:
- Business requirements or user expectations that are not met by the IAG solution or the integrated systems and applications
- Business processes or workflows that are disrupted or delayed by the IAG solution or the integrated systems and applications
- Business rules or policies that are not enforced or applied correctly by the IAG solution or the integrated systems and applications
- Data quality or accuracy issues that affect the IAG solution or the integrated systems and applications
Some best practices to mitigate functional risks are:
- Define and document the business requirements and user expectations for the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, and validate them with the stakeholders
- Design and implement the business processes, workflows, and rules that are supported by the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, following the SAP best practices and standards
- Perform regular testing and validation of the business processes, workflows, and rules that are supported by the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, and resolve any issues or gaps
- Monitor and measure the effectiveness and efficiency of the business processes, workflows, and rules that are supported by the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, and identify any areas for improvement
- Implement and enforce data quality and accuracy standards and controls for the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, and resolve any issues or discrepancies
- Document and review the business processes, workflows, and rules that are supported by the IAG solution and the integrated systems and applications, and maintain a change management process to track any modifications
Organizational Risks:
Organizational risks are related to the people, roles, and responsibilities that are involved in the IAG solution. Some examples of organizational risks are:
- Lack of awareness or understanding of the IAG solution and its benefits among the users or stakeholders
- Lack of skills or competencies to implement, operate, or use the IAG solution among the staff or contractors
- Lack of alignment or coordination among the teams or departments that are involved in the IAG solution
- Lack of ownership or accountability for the IAG solution or the data it processes among the roles or responsibilities
Some best practices to mitigate organizational risks are:
- Communicate and promote the IAG solution and its benefits to the users and stakeholders, and solicit their feedback and input
- Provide adequate training and support to the staff or contractors who are involved in the implementation, operation, or use of the IAG solution, and assess their skills and competencie
- Establish and maintain clear and consistent communication and collaboration channels among the teams or departments that are involved in the IAG solution
- Define and assign clear and specific roles and responsibilities for the IAG solution and the data it processes, and monitor and evaluate their performance and compliance
Compliance Risks:
Compliance risks are related to the legal, regulatory, or contractual obligations that are applicable to the IAG solution or the data it processes. Some examples of compliance risks are:
- Non-compliance with the relevant laws or regulations that govern the access, use, or disclosure of the data that is processed by the IAG solution or the integrated systems and applications
- Non-compliance with the contractual agreements or service level agreements that are established with the customers, partners, or vendors that are involved in the IAG solution or the data it processes
- Non-compliance with the internal policies or standards that are defined by the organization or the industry for the IAG solution or the data it processes
- Non-compliance with the audit or reporting requirements that are imposed by the authorities or the stakeholders for the IAG solution or the data it processes
Some best practices to mitigate compliance risks are:
- Identify and understand the legal, regulatory, or contractual obligations that are applicable to the IAG solution or the data it processes, and ensure that they are met
- Implement and enforce the appropriate controls and safeguards to ensure the compliance of the IAG solution or the data it processes with the relevant laws, regulations, agreements, policies, or standards
- Monitor and document the compliance status and activities of the IAG solution or the data it processes, and report any issues or incidents
- Conduct regular audits and reviews of the IAG solution or the data it processes, and implement any corrective or preventive actions
Use case – SAP SAC
Teams in SAP SAC –
Function in SAP IAG –
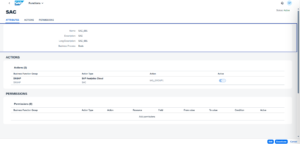
Risk Created in SAP IAG
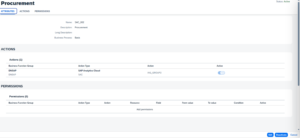
User with Risk is indicated:
Conclusion:
SAP IAG is a powerful and comprehensive solution that can help organizations manage and govern the access rights of their users across various systems and applications. However, implementing and operating IAG also involves some potential risks that need to be identified and mitigated. By following the best practices outlined in this document, organizations can reduce the technical, functional, organizational, and compliance risks associated with IAG, and enhance the value and benefits of the solution